Waves Review
Carry out this review individually. You must answer the questions in the following attachment by exploring the resources that follow and by searching on the internet as you choose.
Waves carry energy from place to place without the transfer of matter.
Travelling waves are organized disturbances that travel with well defined wave speeds. Resource: Traveling vs. standing waves
Types of Waves:
- Mechanical waves require a medium to travel in. Mechanical waves generally move faster through a solid than a liquid and faster through a liquid than a gas.
- Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium. They are self-sustaining oscillations of the electromagnetic field. Examples of electromagnetic waves include radio waves, ultraviolet light, and visible light.
- Resources: Overview of waves from the Physics Classroom; Tour of the Electromagnetic Spectrum; Visible light waves; The electromagnetic spectrum according to NASA
Types of Wave Motion:
- Longitudinal waves are when the particles in the medium move in a parallel direction to the direction in which the wave travels. Sound waves are longitudinal.
- Transverse waves are when the particles in the medium travel perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels. Electromagnetic waves are transverse.
- Resources: Applet of transverse and longitudinal waves; Animations of transverse and longitudinal waves
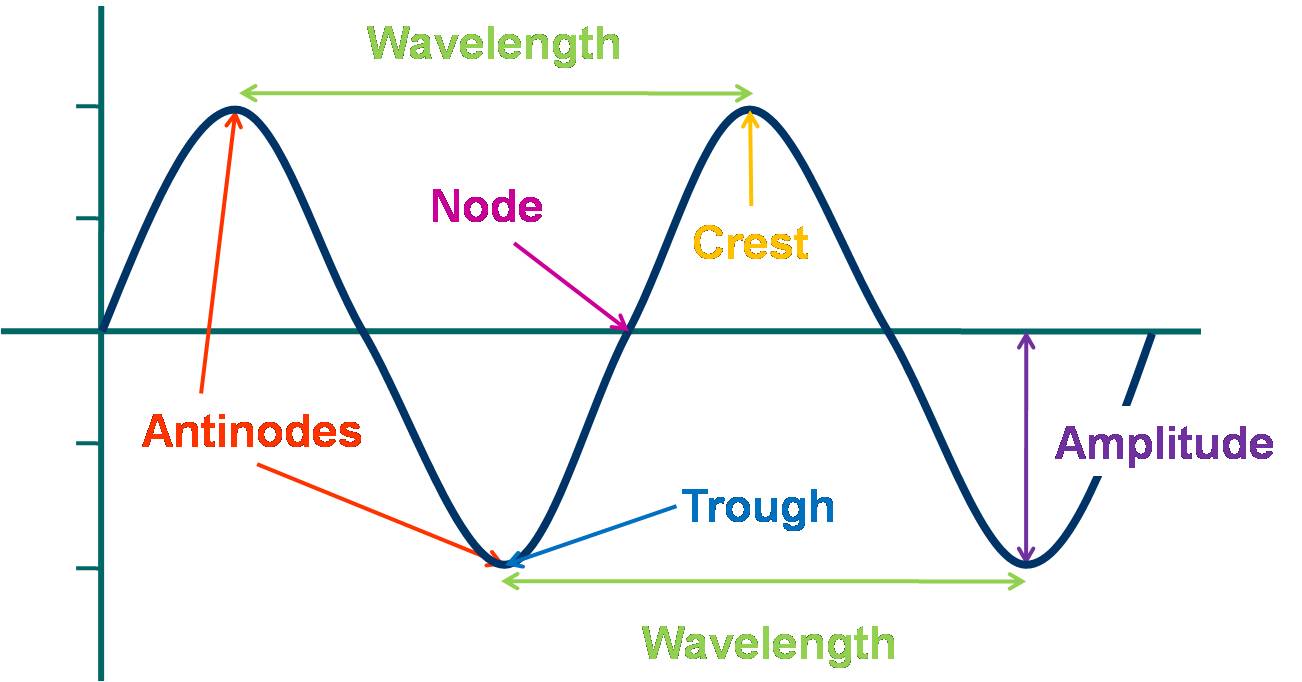
The parts of a wave:
- Node
- Antinode
- Crest
- Trough
How we describe waves:
- Period: The time required for a complete wavelength or cycle to pass a given point. The period of a wave is usually denoted T.
- Frequency: The number of periods or cycles per unit time (usually a second). The frequency is denoted f and is the inverse of a wave’s period. It is measured in Hertz (Hz)
- Phase: This is a given position in the cycle of the wave. It is most commonly used in discussing a “being out of phase” or a “phase shift,” an offset between waves.
- Wavelength: The distance between any two sequential troughs or crests representing a complete cycle in the repeated wave pattern.
- Amplitude: The distance from a wave's antinode to its equilibrium point. This is a measure of the maximum disturbance caused by the wave.
- Resources: Applet of a transverse travelling wave that lets you change amplitude, frequency, and wavelength;
Next Page: